The American Institute of Architects (AIA) Committee on the Environment (COTE) have selected this year’s recipients of the Top Ten Awards, the industry’s premier program celebrating sustainable design excellence. Now in their 21st year, the Top Ten Awards highlight projects that exemplify the integration of great design and great performance. Submissions are required to demonstrate how the project aligns with COTE’s rigorous criteria for social, economic, and ecological value. This year’s recipients will be honored at the 2017 AIA Conference on Architecture in Orlando.
For this year, COTE substantially revised its Measures of Sustainable Design, the criteria judges use to evaluate projects. New topics include impact on health, wellness, and economy. In past years, criteria was based largely on predicted performance, not actual performance as measured after occupying the buildings. Since 2014, past Top Ten recipients have been invited to submit post-occupancy data and narratives to be recognized with a single COTE Top Ten Plus award each year. In 2017, these separate tracks are merged: The ‘Plus’ designation will denote projects with exemplary performance data and post occupancy lessons.
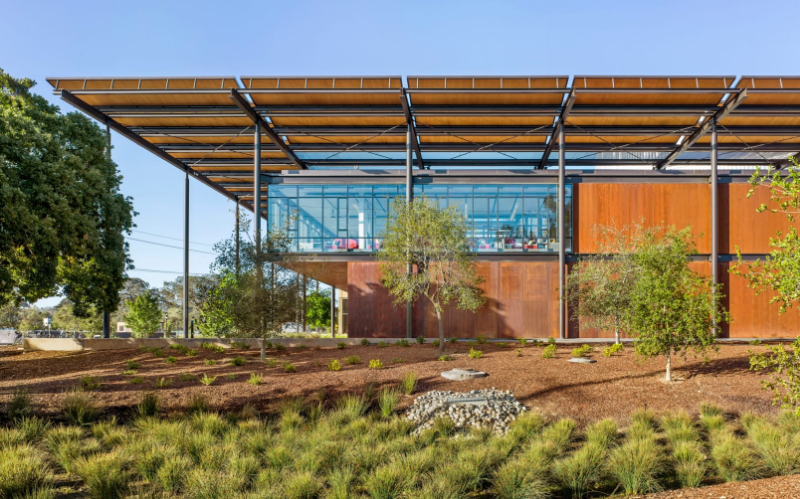
Bristol Community College John J. Sbrega Health and Science Building; Fall River Mass.
Sasaki
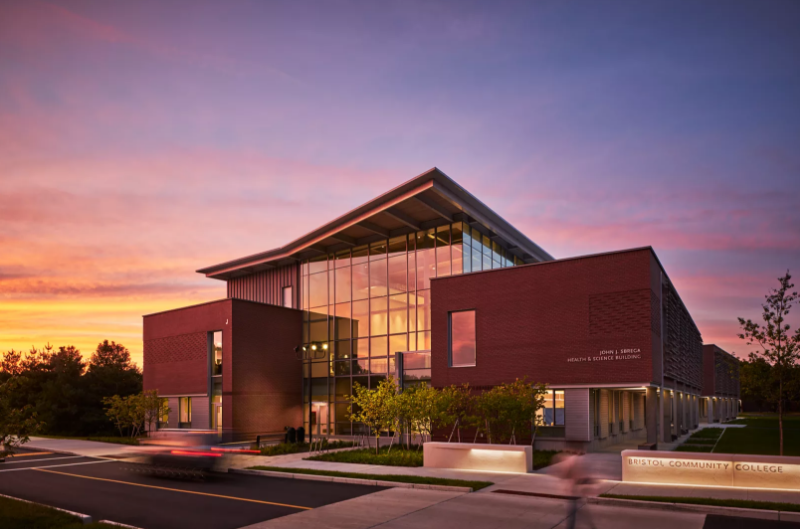 Courtesy Edward Caruso Photography.
Courtesy Edward Caruso Photography.
Bristol set ambitious goals of making its new science building not only elegant and inviting, but also a model of sustainability. The 50,000-square-foot building sets the standard as the first ZNE academic science building in the Northeast. Providing hands-on learning opportunities and care to underserved populations, its program accommodates instructional labs and support space for field biology, biotech, microbiology, and chemistry; nursing simulation labs; clinical laboratory science and medical assisting labs; dental hygiene labs; and a teaching clinic. Taking a holistic approach to the design and construction of the Sbrega Health and Science Building, the team uncovered innovative ways to eliminate the use of fossil fuels, increase efficiency, and dramatically reduce demand.
Brock Environmental Center; Virginia Beach, Va.
SmithGroupJJR
Top Ten Plus honor for exceptional post-occupancy performance
 Photo courtesy Prakash Patel Photography.
Photo courtesy Prakash Patel Photography.
The Brock Environmental Center is a hub for the Chesapeake Bay Foundation’s Hampton Roads office, supporting their education, advocacy and restoration initiatives. The Center is designed to express CBF’s mission of collaboration to protect one of the nation’s most valuable and threatened natural resources – the Chesapeake Bay. CBF aspired to manifest true sustainability, creating a landmark that transcends notions of “doing less harm” towards a reality where architecture can create a positive, regenerative impact on both the environment and society. The Center surpasses LEED achieving zero-net-CO2 emissions, zero waste, and Living Building Challenge certification from the International Living Future Institute.
Chatham University Eden Hall Campus; Richland Township, Penn.
Mithun
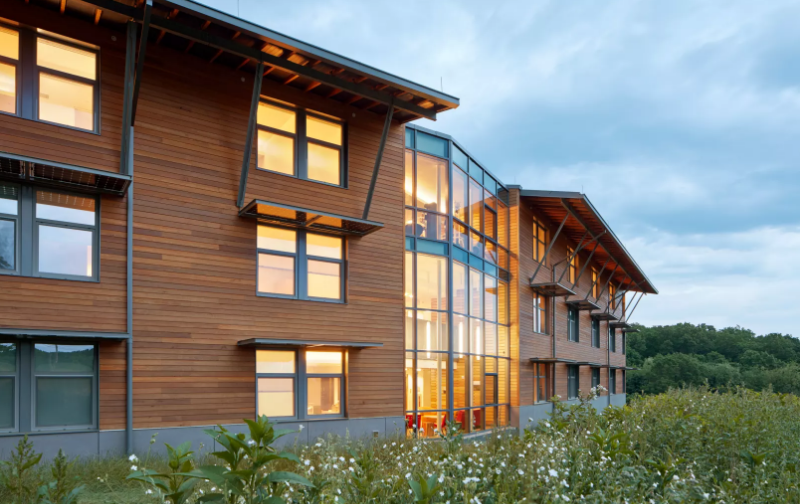 Photo courtesy of Bruce Damonte.
Photo courtesy of Bruce Damonte.
After receiving the donation of 388-acre Eden Hall Farm north of Pittsburgh, Chatham University conceived an audacious goal to create the world’s first net-positive campus. Home of the Falk School of Sustainability, Eden Hall Campus generates more energy than it uses, is a water resource, produces food, recycles nutrients, and supports habitat and healthy soils while developing the next generation of environmental stewards. Linked buildings, landscapes and infrastructure support an active and experiential research environment. New building forms, outdoor gathering spaces and integrated artwork complement and interpret natural site systems, while making cutting-edge sustainable strategies transparent and explicit.
Discovery Elementary School, Arlington Public Schools; Arlington, Va.
VMDO Architects
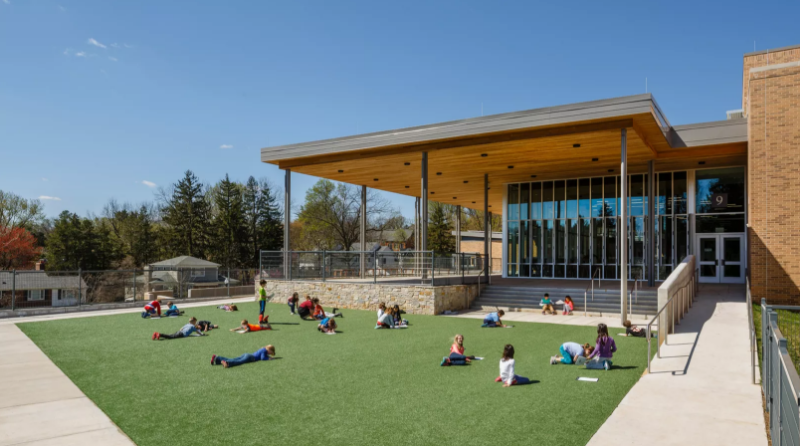 Photo courtesy Alan Karchmer; Lincoln Barbour & VMDO Architects.
Photo courtesy Alan Karchmer; Lincoln Barbour & VMDO Architects.
Discovery Elementary School is the largest zero-energy school in the US. The challenge was to integrate a 98,000 SF building into a residential neighborhood while keeping the entire PV array on the roof. By terracing the mass into a south facing hill, the project met local goals for scale, community goals for preservation of flat, open space for recreation, and global goals for ideal orientation for solar generation. Discovery offers a positive example of a solution to the global crisis of climate change – and along the way emboldens students with the expectation that they are creative participants in those solutions.
Manhattan Districts 1/2/5 Garage & Spring Street Salt Shed; New York City
Dattner Architects and WXY architecture + urban design
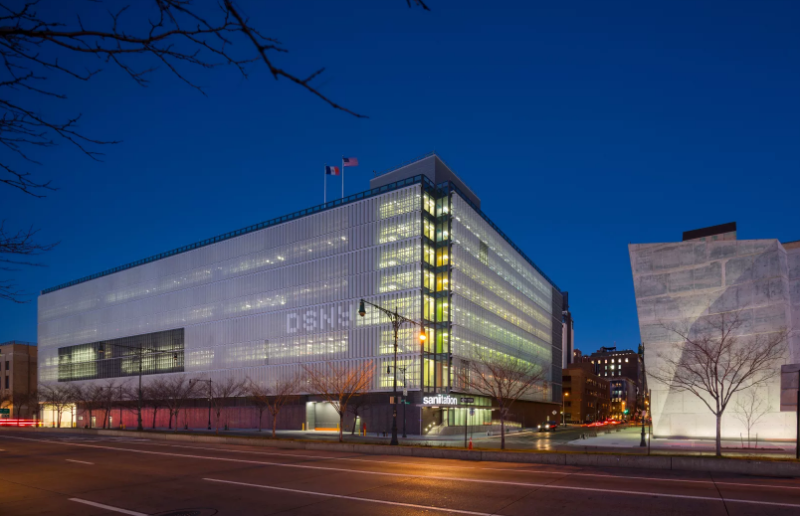

The Garage and Salt Shed celebrate the role of civic infrastructure by integrating innovative architectural design with sustainability and a sensitivity to the urban context. The building is wrapped in a custom perforated double-skin façade that reduces solar gain while allowing daylight and views in personnel areas. The 1.5 acre extensive green roof reduces heat-island effect, promotes biodiversity, and filters waste steam condensate and rainwater allowing it to be reused for truck wash. The projects are also benchmarks for NYC’s Active Design program, which promotes the health and fitness of occupants through building design.
Milken Institute School of Public Health, George Washington University; Washington, D.C.
Payette and Ayers Saint Gross
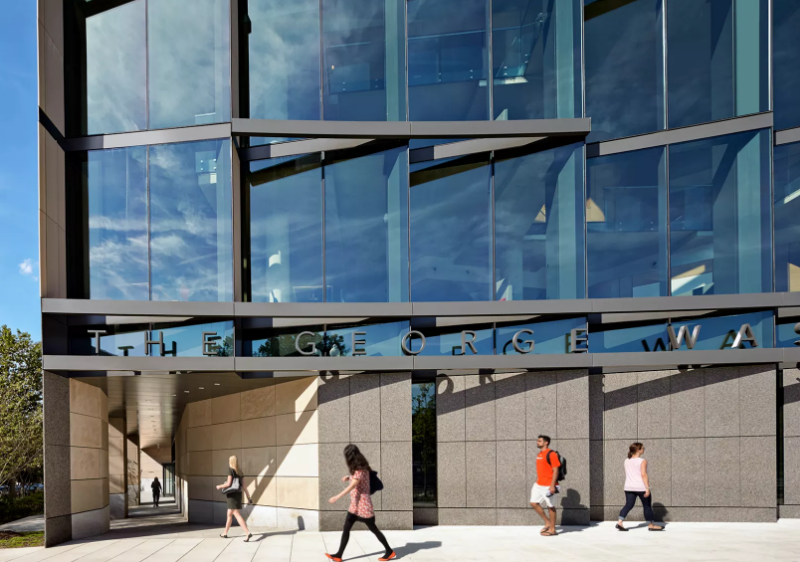 Photo courtesy Robert Benson Photography.
Photo courtesy Robert Benson Photography.
The Milken Institute School of Public Health at GWU embeds core public health values — movement, light/air, greenery, connection to place, social interaction, community engagement — in a highly unconventional, LEED Platinum building on an urban campus in the heart of the nation’s capital. Research offices, classrooms and study areas are clustered around an array of multi-floor void spaces that open the building’s dense core to daylight and views. An irresistible, sky-lit stair ascends all eight levels, encouraging physical activity. The pod-like classrooms are set in from the perimeter so informal study and social interaction space can overlook the bustling traffic circle.
Ng Teng Fong General Hospital & Jurong Community Hospital; Singapore
HOK, USA; CPG, Singapore; Studio 505, Australia
 Photo courtesy Rory Daniel & CPG Consultants.
Photo courtesy Rory Daniel & CPG Consultants.
The Green Mark Platinum NTFGH is part of Singapore’s first medical campus to combine continuing care from outpatient to post-acute care. Based on passive principles, the performance-based design supports resource efficiency, health, and well-being. Seventy percent of the facility is naturally ventilated, representing 82% of inpatient beds. Unlike its Singaporean peers, NTFGH provides every patient with an adjacent operable window, offering daylight and views. An oasis in a dense city, NTFGH incorporates parks, green roofs and vertical plantings throughout the campus. The building uses 38% less energy than a typical Singaporean hospital and 69% less than a typical U.S. hospital.
NOAA Daniel K. Inouye Regional Center; Honolulu
HOK with Ferraro Choi & WSP
 Photo courtesy Alan Karchmer Photography.
Photo courtesy Alan Karchmer Photography.
Located on a national historic landmark site on Oahu’s Ford Island, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Inouye Regional Center features the adaptive reuse of two World War II-era airplane hangars linked by a new steel and glass building. The hangars inspired beautifully simple design solutions for how the center uses air, water and light. The LEED Gold complex accommodates 800 people in a research and office facility that integrates NOAA’s mission of “science, service and stewardship” with Hawaii’s cultural traditions and ecology. The interior environment, which is based on principles of campus design, creates a central gathering place.
R.W. Kern Center; Amherst, Mass.
Bruner/Cott & Associates
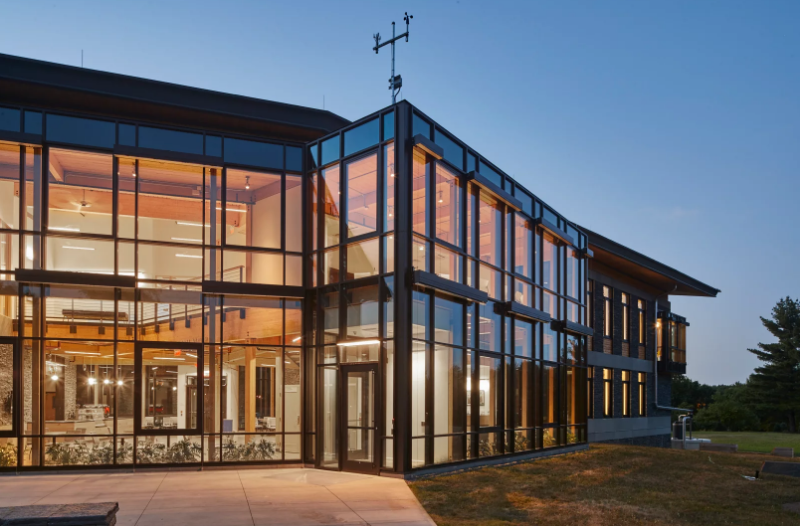 Photo courtesy Robert Benson Photography.
Photo courtesy Robert Benson Photography.
Hampshire College’s R.W. Kern Center is a 17,000-square-foot multi-purpose facility designed to meet the Living Building Challenge. As the gateway to campus, Kern includes classrooms, offices, a café, and gallery space. The building is self-sustaining— generating its own energy, capturing its own water, and processing its own waste. The Kern Center is the result of an inclusive and integrated design process and wholehearted commitment to the environmental mission by the whole team. The project demonstrates Hampshire’s dedication to the highest level of sustainability and stewardship, and to the college’s mission of critical inquiry, active leadership and hands-on learning.
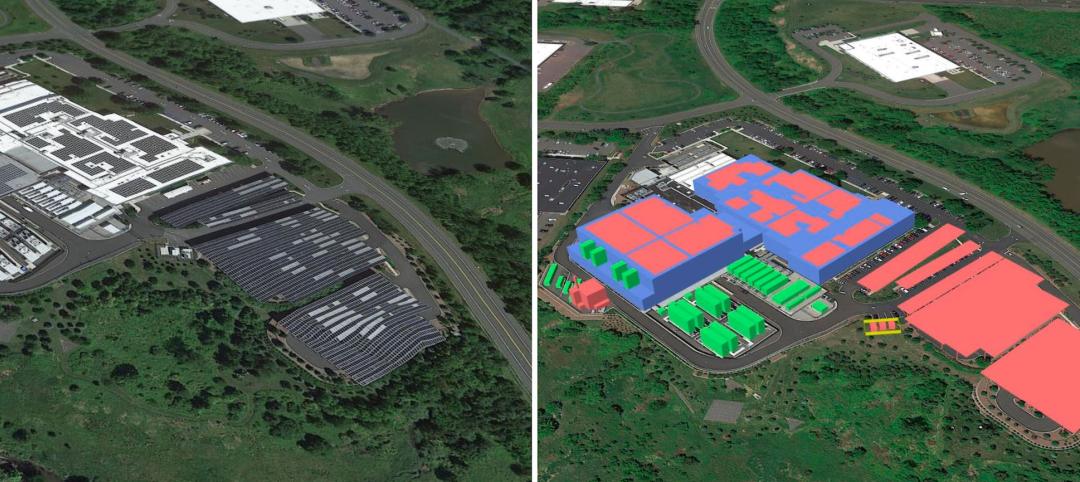
Stanford University Central Energy Facility; Stanford, Calif.
ZGF Architects LLP
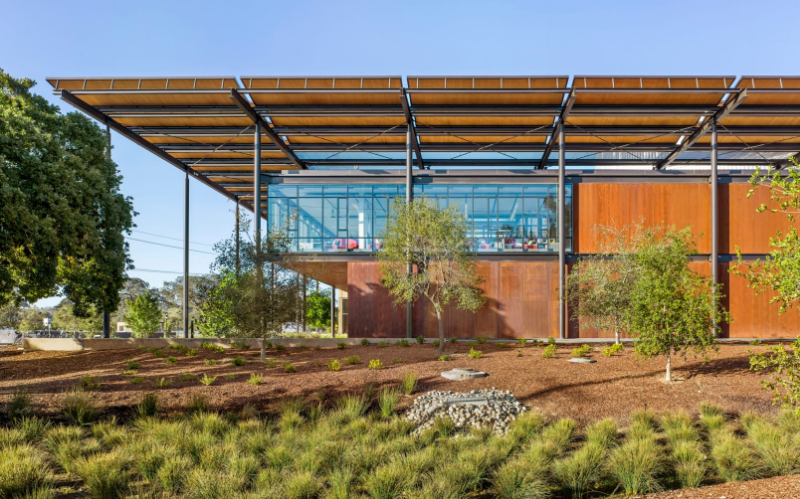 Photo courtesy Robert Canfield.
Photo courtesy Robert Canfield.
At the heart of Stanford University’s transformational, campus-wide energy system is a new, technologically advanced central energy facility. The system replaces a 100% fossil-fuel-based cogeneration plant with primarily electrical power—65% of which comes from renewable sources—and a first-of-its-kind heat recovery system, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and fossil fuel and water use. The facility comprises a net-positive-energy administrative building, a heat recovery chiller plant, a cooling and heating plant, a service yard, and a new campus-wide main electrical substation. Designed to sensitively integrate into the surrounding campus, the architectural expression is one of lightness, transparency and sustainability to express the facility’s purpose.
Related Stories
Sustainability | Jul 19, 2023
California lawmakers approve governor’s plan to accelerate green construction
California lawmakers recently approved Gov. Gavin Newsom’s infrastructure streamlining plan that aims to accelerate clean energy and infrastructure projects.
Sustainability | Jul 13, 2023
Deep green retrofits: Updating old buildings to new sustainability standards
HOK’s David Weatherhead and Atenor’s Eoin Conroy discuss the challenges and opportunities of refurbishing old buildings to meet modern-day sustainability standards.
Mass Timber | Jul 11, 2023
5 solutions to acoustic issues in mass timber buildings
For all its advantages, mass timber also has a less-heralded quality: its acoustic challenges. Exposed wood ceilings and floors have led to issues with excessive noise. Mass timber experts offer practical solutions to the top five acoustic issues in mass timber buildings.
Adaptive Reuse | Jul 6, 2023
The responsibility of adapting historic university buildings
Shepley Bulfinch's David Whitehill, AIA, believes the adaptive reuse of historic university buildings is not a matter of sentimentality but of practicality, progress, and preservation.
Contractors | Jun 30, 2023
Construction industry task force aims for standardized carbon reporting
A newly formed Associated General Contractors of America (AGC) task force on decarbonization and carbon reporting will address the challenges around reporting and reducing carbon emissions in the construction industry.
Apartments | Jun 27, 2023
Dallas high-rise multifamily tower is first in state to receive WELL Gold certification
HALL Arts Residences, 28-story luxury residential high-rise in the Dallas Arts District, recently became the first high-rise multifamily tower in Texas to receive WELL Gold Certification, a designation issued by the International WELL Building Institute. The HKS-designed condominium tower was designed with numerous wellness details.
Green | Jun 26, 2023
Federal government will spend $30 million on novel green building technologies
The U.S. General Services Administration (GSA), and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) will invest $30 million from the Inflation Reduction Act to increase the sustainability of federal buildings by testing novel technologies. The vehicle for that effort, the Green Proving Ground (GPG) program, will invest in American-made technologies to help increase federal electric vehicle supply equipment, protect air quality, reduce climate pollution, and enhance building performance.
Industrial Facilities | Jun 20, 2023
A new study presses for measuring embodied carbon in industrial buildings
The embodied carbon (EC) intensity in core and shell industrial buildings in the U.S. averages 23.0 kilograms per sf, according to a recent analysis of 26 whole building life-cycle assessments. That means a 300,000-sf warehouse would emit 6,890 megatons of carbon over its lifespan, or the equivalent of the carbon emitted by 1,530 gas-powered cars driven for one year. Those sobering estimates come from a new benchmark study, “Embodied Carbon U.S. Industrial Real Estate.”
Mechanical Systems | Jun 16, 2023
Cogeneration: An efficient, reliable, sustainable alternative to traditional power generation
Cogeneration is more efficient than traditional power generation, reduces carbon emissions, has high returns on the initial investment, improves reliability, and offers a platform for additional renewable resources and energy storage for a facility. But what is cogeneration? And is it suitable for all facilities?
Resiliency | Jun 14, 2023
HUD offers $4.8 billion in funding for green and resilient building retrofit projects
The Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) recently released guidelines for its Green and Resilient Retrofit Program (GRRP) that has $4.8 billion for funding green projects.