In its latest Technology Outlook, oil and gas giant BP predicted batteries for vehicles and electricity-grid applications could have “significant potential to influence future fossil-fuel demand in the transport sector and enable greater penetration of intermittent renewable energy.”
A convergence of events is making batteries affordable and even desirable as catalysts for nudging consumers, industries, and nations from carboncentric energy consumption.
The Department of Energy’s Joint Center for Energy Storage Research is working on prototypes for transportation and the grid that, when scaled to manufacturing, would deliver five times the energy density at one-fifth the cost of commercial batteries available when the Joint Center launched in 2012.
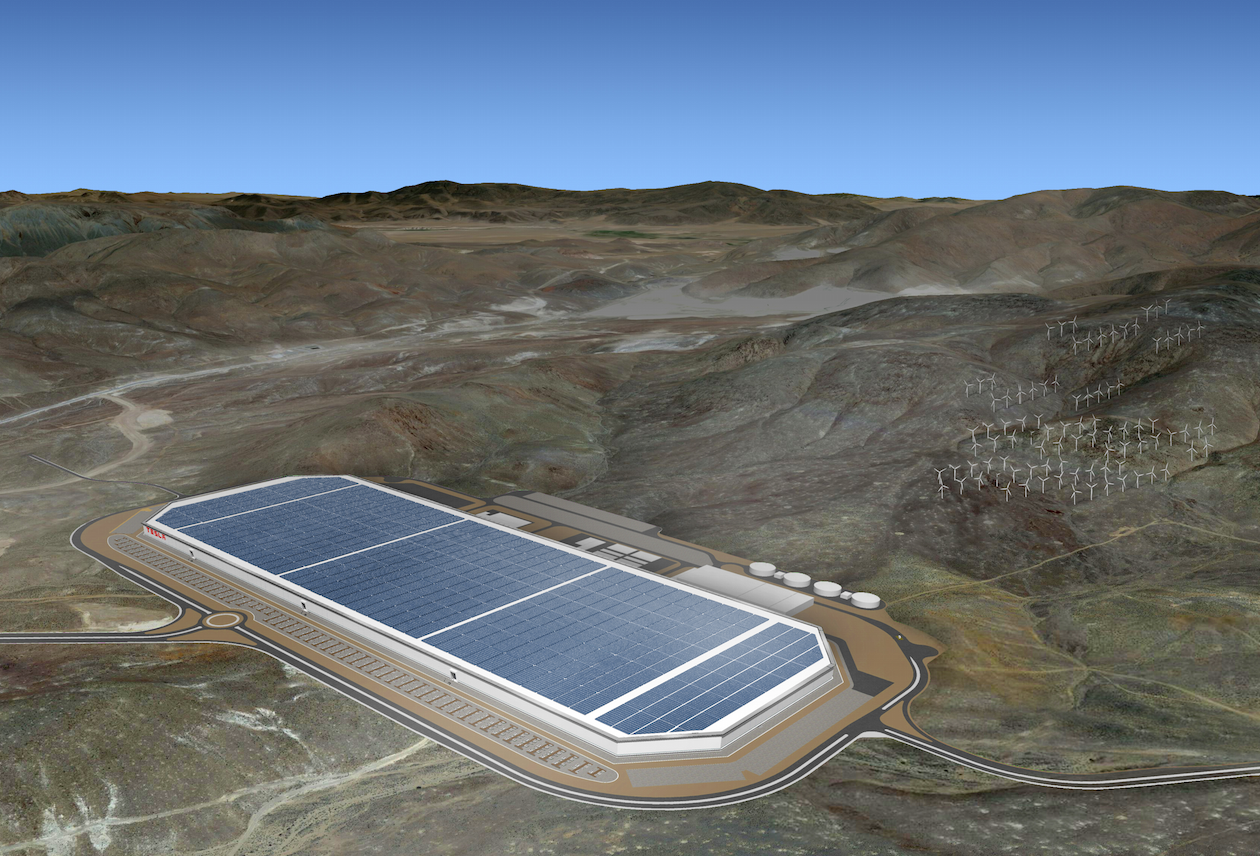
What’s really put batteries in the spotlight, though, is the Gigafactory that Tesla Motors is building near Reno, Nev., and expects to open this year. When it reaches full capacity in 2020, this $5 billion, 13.6 million-sf plant could be producing enough lithium-ion battery packs annually to equal 50 gigawatt hours of storage, or more than what had been produced worldwide in 2013.
Tesla’s CEO Elon Musk told Fast Company that advancements in battery technology would be “incremental.” But Musk is confident his company can lower battery cost by at least 30% through mass production. “The fundamental focus is the cost per unit of energy,” he told Tech Insider.
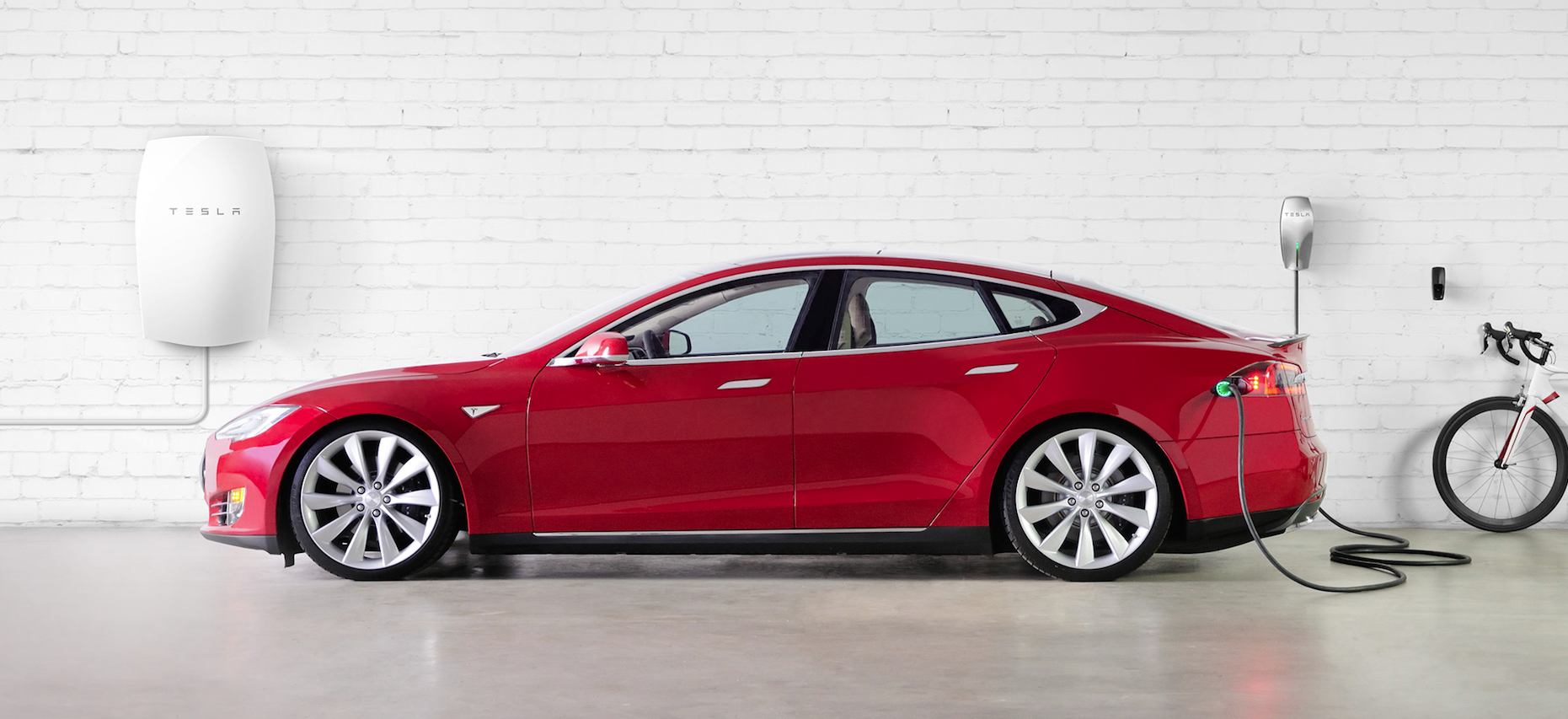 Last April, Tesla rolled out Powerwall, a rechargeable lithium-ion battery for residential use.
Last April, Tesla rolled out Powerwall, a rechargeable lithium-ion battery for residential use.
Last April, Tesla rolled out Powerwall, a rechargeable lithium-ion battery for residential use. One model, retailing for $3,500, offers 10kWh capacity for backup applications; a second model, for $3,000, has 7kWh peak capacity for daily-cycle applications. Tesla’s Powerpack, for commercial use, can store up to 100kWh of electricity, and retails for around $25,000.
Tesla positions batteries as less-expensive ways for homeowners and businesses to store power collected by solar PV arrays during the day for use at night. If battery energy storage proliferates, Musk believes that 10% of the world’s fossil-fuel power plants could be mothballed within years.
“The goal has not been: Let’s make cars; the goal has been: We need to accelerate the advent of sustainable energy,” Musk said. Still, Tesla is creating demand by expanding its electric-car plant in Fremont, Calif., to pump out 500,000 cars per year by 2020.
Batteries for energy storage are already elbowing their way into the commercial mainstream, says Garrett Fitzgerald, Senior Associate with the Rocky Mountain Institute. They are being deployed in the PJM wholesale electricity market for frequency regulation, and in California for demand-charge reduction to smooth out energy loads.
Janice Lin, Co-founder of Strategen Consulting and Executive Director of the California Energy Storage Alliance, foresees battery energy storage as the next tool for property managers to control energy, deliver services when occupants demand it, and make money in the process. And battery energy storage is economically feasible in markets where feed-in tariffs, which offer producers a set price for renewable energy returned to the grid, have been dropping.
A big part of Tesla’s game plan is to stimulate public acceptance of solar energy, which accounts for 1% of U.S. electricity output but is expanding. As of the second quarter of 2015, 22.7 gigawatts of solar capacity had been installed, and another 20,000 megawatts are forecast to come online in 2015-16, according to the Solar Energy Industries Association. Residential solar costs have dropped 45% since 2010, and utility-scale solar has fallen even more, to where recent contract prices are below 5 cents/kWh.
In its $1.1 trillion spending bill, passed on December 18, Congress included a five-year extension of the 30% solar investment tax credit, which was set to expire for residential and decline to 10% for commercial at the end of 2016. Bloomberg New Energy Finance had estimated that new commercial and industrial solar capacity would be nearly 18% less from 2015 through 2022 under a lower tax credit. New residential capacity would be 31% less without the tax credit.
Related Stories
AEC Tech | Mar 14, 2023
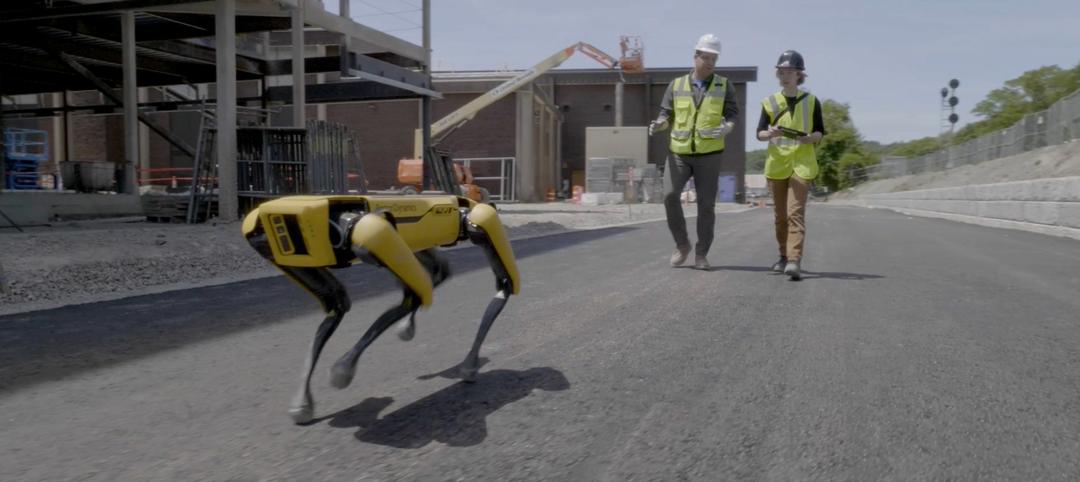
Skanska tests robots to keep construction sites clean
What if we could increase consistency and efficiency with housekeeping by automating this process with a robot? Introducing: Spot.
Modular Building | Mar 3, 2023
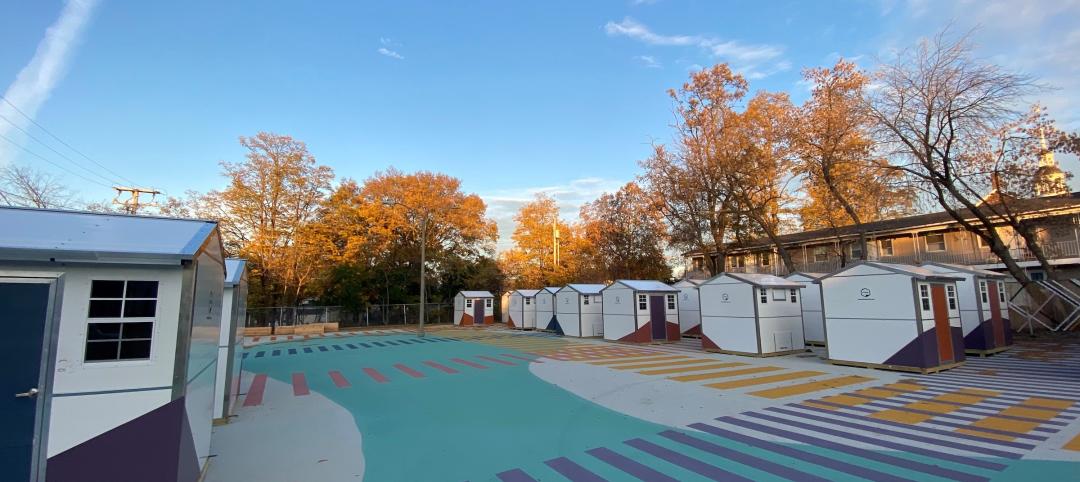
Pallet Shelter is fighting homelessness, one person and modular pod at a time
Everett, Wash.-based Pallet Inc. helped the City of Burlington, Vt., turn a municipal parking lot into an emergency shelter community, complete with 30 modular “sleeping cabins” for the homeless.
AEC Tech | Jan 27, 2023
Epic Games' latest foray into the AEC market and real estate industry
From architecture to real estate, the realm of computer-aided design hits new heights as more and more firms utilize the power of Epic Games’ Twinmotion and Unreal Engine.
AEC Tech | Jan 27, 2023
Key takeaways from Autodesk University 2022
Autodesk laid out its long-term vision to drive digital collaboration through cloud-based solutions and emphasized the importance of connecting people, processes and data.
AEC Tech Innovation | Jan 24, 2023
ConTech investment weathered last year’s shaky economy
Investment in construction technology (ConTech) hit $5.38 billion last year (less than a 1% falloff compared to 2021) from 228 deals, according to CEMEX Ventures’ estimates. The firm announced its top 50 construction technology startups of 2023.
AEC Tech | Jan 19, 2023
Data-informed design, with Josh Fritz of LEO A DALY
Joshua Fritz, Leo A Daly's first Data Scientist, discusses how information analysis can improve building project outcomes.
AEC Tech Innovation | Jan 14, 2023
CES recognizes a Dutch firm’s wearable technology for construction management
The firm’s TokenMe product offers construction managers a real-time crowd- and asset-tracking solution via low-power, location-aware radio and RFID tags and multiple sensors through which data are processed with cloud-based artificial intelligence.
Digital Twin | Nov 21, 2022
An inside look at the airport industry's plan to develop a digital twin guidebook
Zoë Fisher, AIA explores how design strategies are changing the way we deliver and design projects in the post-pandemic world.
Giants 400 | Nov 14, 2022
4 emerging trends from BD+C's 2022 Giants 400 Report
Regenerative design, cognitive health, and jobsite robotics highlight the top trends from the 519 design and construction firms that participated in BD+C's 2022 Giants 400 Report.
Contractors | Nov 14, 2022
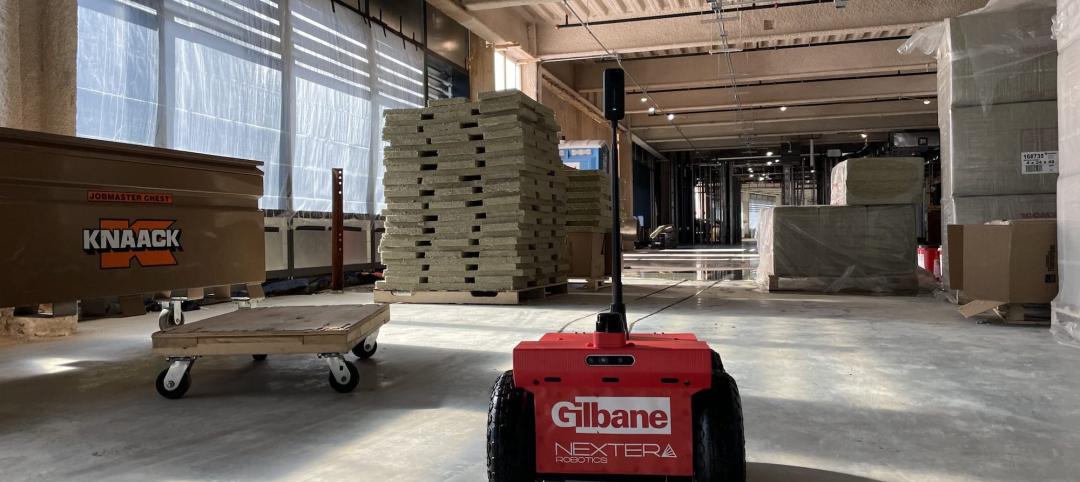
U.S. construction firms lean on technology to manage growth and weather the pandemic
In 2021, Gilbane Building Company and Nextera Robotics partnered in a joint venture to develop an artificial intelligence platform utilizing a fleet of autonomous mobile robots. The platform, dubbed Didge, is designed to automate construction management, maximize reliability and safety, and minimize operational costs. This was just one of myriad examples over the past 18 months of contractor giants turning to construction technology (ConTech) to gather jobsite data, manage workers and equipment, and smooth the construction process.