Anyone who has driven for any considerable length in bad winter weather has had that moment of panic when one second you feel completely in control of the automobile and the next you feel like a bull rider just trying to hang on for dear life.
Hitting a patch of black ice is scary enough when the outcome is nothing more than a brief moment of wheel spin or slight fishtailing. But the end result to a slippery, snow-covered road can be far worse. From fender benders to fatal accidents, driving in bad winter weather is downright dangerous.
Enter Dr. Chris Tuan, a professor of civil engineering at the University of Nebraska. Tuan has designed a new type of concrete that has the ability to carry a small electric current in order to generate enough heat to melt snow and ice from its own surface, reports the Huffington Post.
The concrete mixture is made up of about 20% steel shavings and carbon particles. This 20% is what allows the concrete to conduct electricity, thus giving it its superpower.
All that needs to be done is to connect the de-icing concrete slabs to a power source and watch them do their job. The electrical resistance in the concrete generates the heat, which in turn melts the snow and ice on its surface.
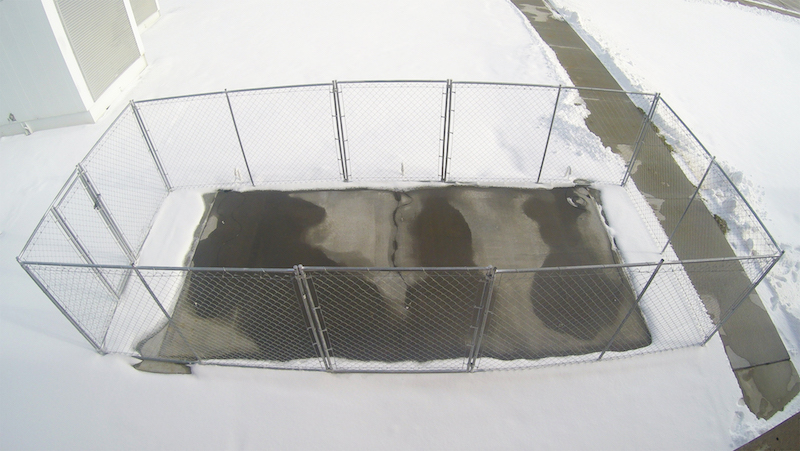 Photo: Chris Tuan and Lim Nguyen
Photo: Chris Tuan and Lim Nguyen
The de-icing concrete doesn’t come without its extra costs, however. While regular concrete costs about $120 per cubic yard, Tuan’s concrete is more than double that, at about $300 per cubic yard. So, at least for the time being, the cost of the concrete means it will be used sparingly and just in the areas that need it most.
“De-icing concrete is intended for icy bridges, street intersections, interstate exit ramps, and where accidents are prone to take place,” said Tuan in an interview with UNL. “It’s not cost-effective to build entire roadways using conductive concrete, but you can use it at certain locations where you always get ice.”
Other possible areas of use would be parking lots and airports. Who hasn’t been walking to their car in the morning, after successfully dragging yourself out of bed, only to take that first step into the parking lot just to have your foot slip right out from under your body? That morning walk to the car in the sub-freezing temperatures would be made at least a little bit better if you didn’t have to do it looking like a fawn learning to walk for the first time.
While airports wouldn’t use the new concrete for their runways, it could still help prevent delays during bad weather.
“What they need is the tarmac around the gated areas cleared, because they have so many carts to unload—luggage service, food service, trash service, fuel service—that all need to get into those areas,” Tuan said. “They said that if we can heat that kind of tarmac, then there would be (far fewer) weather-related delays.”
This concrete technology is already in use in a 150-foot bridge near Lincoln, Neb. In 2002, the bridge was inlaid with 52 slabs of the de-icing concrete and has been very successful in melting snow and ice.
While it has the potential to save lives, this de-icing technology has practical, convenient uses, as well. “I have a patio in my backyard that is made of conductive concrete. So I’m practicing what I preach,” Tuan said.
While snowplows and shovels haven’t been rendered useless yet, this new technology has plenty of benefits to help keep people safe during bad winter weather.
Related Stories
| Nov 22, 2011
New Green Matters Conference examines emerging issues in concrete and sustainability
High-interest topics will be covered in technical seminars, including infrared reflective coatings for heat island mitigation, innovative uses of concrete to provide cooling and stormwater management, environmental benefits of polished concrete, and advancements in functional resilience of architectural concrete.
| Nov 16, 2011
CRSI recommends return to inch-pound markings
The intention of this resolution is for all new rollings of reinforcing steel products to be marked with inch-pound bar markings no later than January 1st, 2014.
| Nov 8, 2011
Transforming a landmark coastal resort
Originally built in 1973, the building had received several alterations over the years but the progressive deterioration caused by the harsh salt water environment had never been addressed.
| Nov 8, 2011
WEB EXCLUSIVE: Moisture-related failures in agglomerated floor tiles
Agglomerated tiles offer an appealing appearance similar to natural stone at a lower cost. To achieve successful installations, manufacturers should provide design data for moisture-related dimensional changes, specifiers should require in-situ moisture testing similar to those used for other flooring materials, and the industry should develop standards for fabrication and installation of agglomerated tiles.
| Nov 2, 2011
CRSI’s Manual of Standard Practice now available
This resource contains information on recommended industry practices for estimating, detailing, fabricating, and placing reinforcing steel for reinforced concrete construction.
| Nov 1, 2011
Holcim awards winners for North America announced
A socio-architectural project to create regional food-gathering nodes and a logistics network in Canada's high arctic territory won the top prize for North America of $100,000.
| Oct 14, 2011
ACI partners with CRSI to launch new adhesive anchor certification program
Adhesive anchor installer certification required in new ACI 318-11.
| Oct 7, 2011
GREENBUILD 2011: Transparent concrete makes its North American debut at Greenbuild
The panels allow interior lights to filter through, from inside.
| Oct 4, 2011
GREENBUILD 2011
Click here for the latest news and products from Greenbuild 2011, Oct. 4-7, in Toronto.
| Sep 20, 2011
Jeanne Gang wins MacArthur Fellowship
Jeanne Gang, a 2011 MacArthur Fellowship winner described by the foundation as "an architect challenging the aesthetic and technical possibilities of the art form in a wide range of structures."