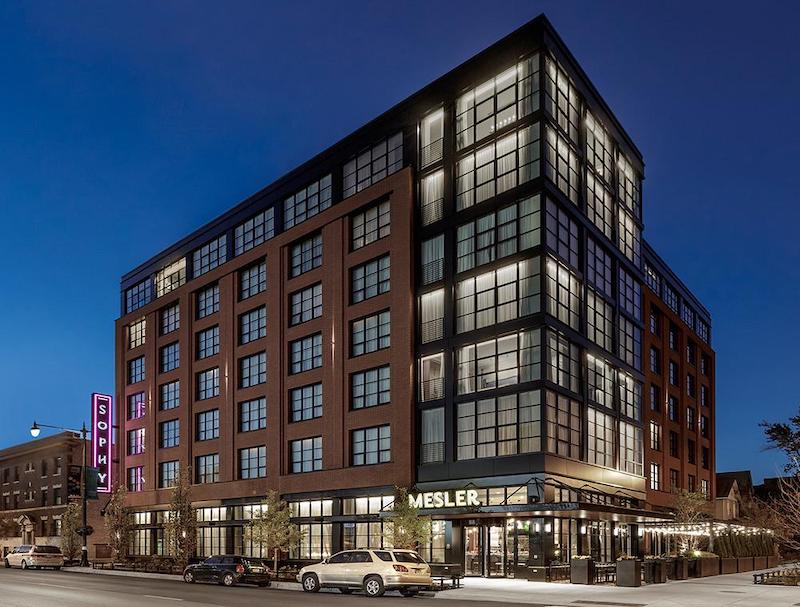
The Sophy Hotel, Chicago Hyde Park’s newest boutique hotel, takes its name from the Greek word sophia, meaning knowledge and science. Completed in 2018, the seven-story, 98-guest room hotel complements the local museums, cultural attractions, and University of Chicago campus. The ground floor features 14-foot ceilings in a column-free lobby, lounge, and restaurant space; Floors two to seven include guest rooms and amenities. While the project driver during design and construction was using prefabricated, cold-formed metal framing (CFMF) wall panels, structural steel became an integral component of the building construction. This article highlights how steel was used 1) at the second-floor podium to transfer the upper levels 2) embedded within the CFMF system to create unique upper level spaces, and 3) to support exterior appendages and articulated brick veneer.
Sophy Hotel Utilizes Steel Podium Design
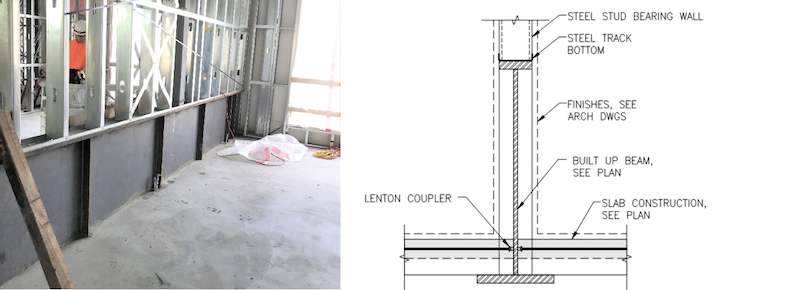
The second to seventh floors are guest rooms with stacked CFMF walls at the demising walls. Below the second floor, the program changes to a lobby, restaurant, and back-of-house space requiring a column-free footprint, which creates a vertical framing discontinuity. The discontinuity demands a transfer structure at the second floor.
Deep structural steel beams offer the strength and stiffness requirements for the long spans to create the open footprint. The framing generally consists of 40 in. deep, wide-flange shapes spanning up to 35 ft between perimeter steel columns and interior concrete masonry unit (CMU) core walls. The podium steel framing aligns with the CFMF wall system above. The podium framing depth is governed by serviceability limits and the ceiling height required below. To minimize global displacement and potential cracking in the gypsum wall board (GWB) sheathing on the CFMF bearing walls, total deflections at the podium level are limited to the smaller of L/1000 or 3/8 in. After accounting for a 14 ft ceiling at the ground floor and six levels of guest rooms within the 80 ft building height, a 3 ft – 8 in. space was available above the ground floor ceiling. This space is used to accommodate the steel transfer framing, mechanical ductwork, plumbing, electrical conduit, and fire protection services.
The Sophy Hotel's podium design maximized steel framing depth to accommodate beam web penetrations for the building services with the ceiling framing supported directly to the steel beam bottom flanges. While providing beam web penetrations for building services is common industry practice, in a depth-constrained podium structure, it is important to have early and on-going coordination between design and construction disciplines to avoid the need for field cutting beam web penetrations in the podium framing.
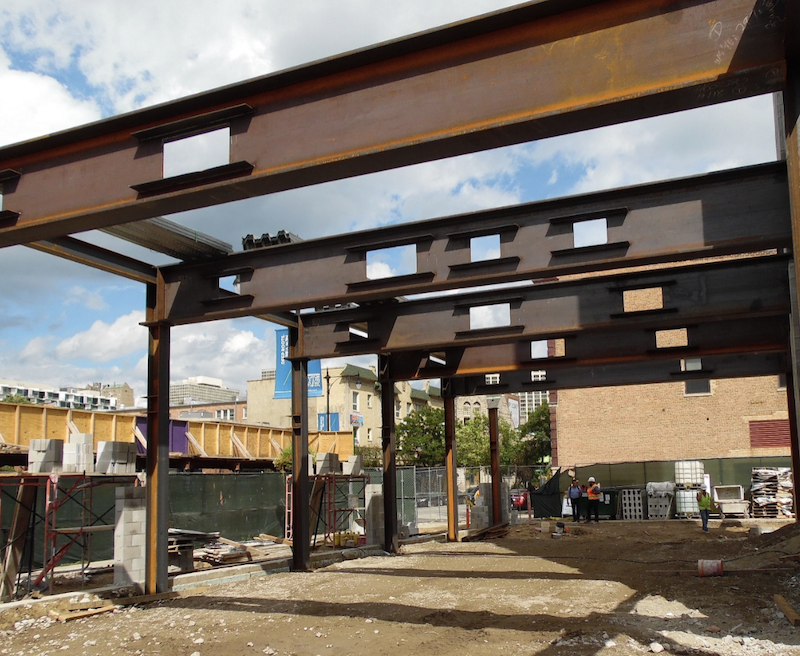 Beam web penetrations in steel podium framing.
Beam web penetrations in steel podium framing.
Upturned Framing
CFMF wall systems are most efficient when the wall panels align from the lowest level of support to the roof. Aligning wall panels requires a vertically repetitive program. Breaking up the repetitive program for open space amenities may require removing bearing walls and transferring the bearing wall load. One way to transfer the load while maintaining slab depth and without compromising ceiling heights is to provide upturned steel framing.
At the Sophy Hotel, the fitness room and laundry room are located on the second floor, each occupying a space twice the width of the typical guest room. To eliminate bearing walls on the second floor at these locations, steel columns are extended above the podium structure to support upturned, built-up plate girders. The plate girders support the bearing walls between the third floor and roof level while providing space on the second floor for the fitness room and laundry room. Built-up shapes are used to accommodate the architectural program constraints. The plate girders comprise a 6 in. wide top flange to match the width of the CFMF wall and a wider bottom flange to support the floor construction.
 Upturned steel built-up plate girder above the fitness room.
Upturned steel built-up plate girder above the fitness room.
On a smaller scale, upturned WT5x15s span across the corridor between CFMF wall panels, with the slab construction supported on the flange, and the stem embedded within the concrete slab. This detail maximizes ceiling heights along the corridors and provides a continuous horizontal space for building services.
Steel in CFMF Walls
Structural steel framing is integrated within the CFMF wall systems to address atypical support conditions and large openings. At the sixth and seventh floors, two CFMF walls are eliminated to combine two guest rooms into an open space suite. Structural steel frames comprised of wide flange beams and HSS columns are provided in lieu of the CFMF walls to create the open space. The frame columns extend down to the podium and are fabricated into the CFMF wall panels with base plates and cap plates. In some areas, HSS headers are provided within the CFMF wall panels to span large door openings. Structural steel when required for larger spans, allows for the flexibility the program required.
Exterior Wall Support
The building envelope generally consists of articulated brick masonry veneer with large punched windows. The veneer steps around the windows creating three different vertical planes. The planes converge at vertical piers between windows. The floor construction spans from CFMF wall-to-wall without steel framing at the slab edge. To avoid a stepped slab edge and steel relieving angles, the design team balloon-framed the masonry veneer from an independent, architecturally exposed structural steel (AESS) frame at the second floor. Custom bent plate loose lintels are used above the window openings to accommodate the varying planes of masonry.
The typical AESS frame comprises a MC18x42.7, HSS20x8 and HSS6x4 knee wall spanning between CMU piers. The frame is braced at the ends and mid-span to the podium structure to resist the eccentric brick loads.
 AESS structure supporting the balloon-framed brick veneer.
AESS structure supporting the balloon-framed brick veneer.
Building Appendages
The hotel features a three-story tall marquee extending from the building corner. The sign structural support includes an HSS10x6 post that extends from the second-floor steel podium to the fifth-floor, and HSS outriggers at the sign support locations. The HSS post is detailed with deck support plates and weldable rebar couplers at each floor level to drag the sign forces into the building diaphragm.
The hotel also features an 18 ft entry canopy supported at the second floor with a side-plated W40 beam and by four diagonal tie-rods pinned to HSS10x4 flat outriggers at the third floor. The outriggers are supported on HSS posts fabricated within the CFMF wall panel and extend into the third-floor slab construction with headed studs and hair pin reinforcement to drag the horizontal load into the third-floor diaphragm.
 Entrance canopy structure and marquee. Photo: Mark Ballogg.
Entrance canopy structure and marquee. Photo: Mark Ballogg.
Conclusions
The structural steel framing in the construction of the Sophy Hotel is an integral component of the building structure alongside the prefabricated CFMF wall systems. It allows the building structural design to achieve the economy of repetition while creating opportunities for architectural freedom.
Related Stories
| Apr 30, 2013
Healthcare lighting innovation: Overhead fixture uses UV to kill airborne pathogens
Designed specifically for hospitals, nursing homes, child care centers, and other healthcare facilities where infection control is a concern, the Arcalux Health Risk Management System (HRMS) is an energy-efficient lighting fixture that doubles as a germ-killing machine.
| Apr 24, 2013
North Carolina bill would ban green rating systems that put state lumber industry at disadvantage
North Carolina lawmakers have introduced state legislation that would restrict the use of national green building rating programs, including LEED, on public projects.
| Apr 24, 2013
Los Angeles may add cool roofs to its building code
Los Angeles Mayor Antonio Villaraigosa wants cool roofs added to the city’s building code. He is also asking the Department of Water and Power (LADWP) to create incentives that make it financially attractive for homeowners to install cool roofs.
| Apr 10, 2013
ASHRAE publishes second edition to HVAC manual for healthcare facilities
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) has published a second edition of its “HVAC Design Manual for Hospitals and Clinics.”
| Apr 2, 2013
6 lobby design tips
If you do hotels, schools, student unions, office buildings, performing arts centers, transportation facilities, or any structure with a lobby, here are six principles from healthcare lobby design that make for happier users—and more satisfied owners.
| Apr 2, 2013
4 hospital lobbies provide a healthy perspective
A carefully considered entry zone can put patients at ease while sending a powerful branding message for your healthcare client. Our experts show how to do it through four project case studies.
| Mar 29, 2013
Detroit's historic Whitney Building to be renovated for hotel, apartments
Detroit's David Whitney Building, a 19-story landmark erected in 1915, will be renovated for an Aloft hotel and apartments.
| Mar 29, 2013
Cuningham Group acquires NTD's healthcare practice, expands into key markets
The international design firm Cuningham Group Architecture, Inc. has announced that NTD Healthcare has the joined the company in a strategic expansion. A practice of NTD Architecture, NTD Healthcare joins Cuningham Group with three principals: Wayne Hunter, AIA, NCARB, ACHA and Phillip T. Soule, III, AIA, ACHA in San Diego, along with Maha Abou-Haidar, AIA in Phoenix.
| Mar 15, 2013
7 most endangered buildings in Chicago
The Chicago Preservation Society released its annual list of the buildings at high risk for demolition.
| Mar 14, 2013
25 cities with the most Energy Star certified buildings
Los Angeles, Washington, D.C., and Chicago top EPA's list of the U.S. cities with the greatest number of Energy Star certified buildings in 2012.

















