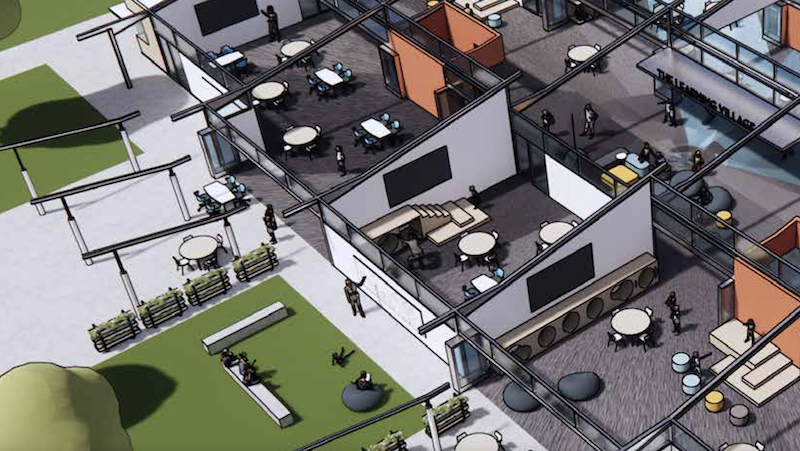
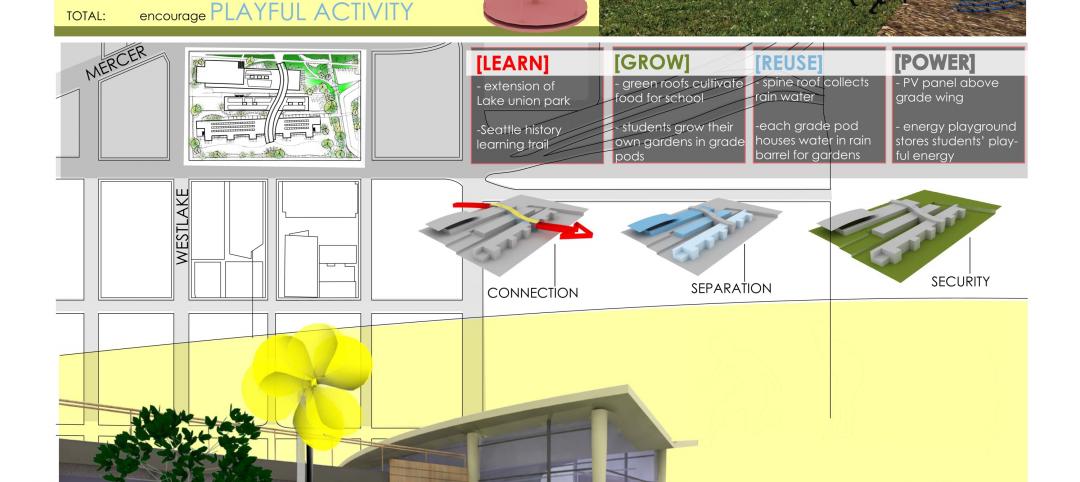
As school children have returned to classrooms, school districts are rethinking how outdoor spaces can support the safe return of in-person instruction and lower the risk of virus transmission.
To that end, the Los Angeles County Office of Education has published a 53-page report that provides K-12 schools with Design Guidelines for Outdoor Learning Environments. The AEC firms HMC Architects, the landscape architect AHBE|MIG, the engineering consultant IMEG, and the construction manager Bernards assisted the county in putting together this content.
“Outdoor learning has been proven to offer students a range of benefits, from enhancing engagement to reducing stress and promoting physical and psychological wellbeing,” says Dr. Debra Duardo, Los Angeles County Superintendent of Schools, in the report’s introduction. “When we take lessons outside our classroom walls, we teach our children that learning can happen anywhere and anytime, promoting lifelong curiosity.
“My commitment,” she continues, “is to advocate for a collective investment in such approaches, surrounding our most vulnerable students with the resources they need to succeed and fostering positive, healthy learning environments. Increasing opportunities for outdoor learning is essential to advancing educational equity.”
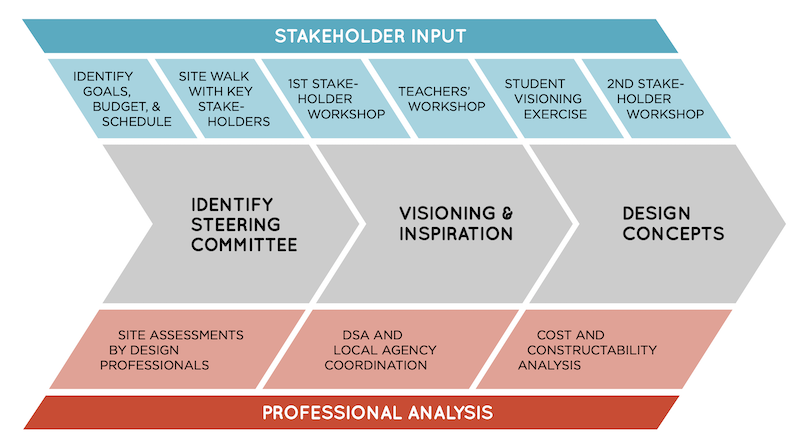 This schematic shows how various stakeholders can be engaged when devising how schools should design outdoor learning environments. Charts and graphics: Los Angeles County Office of Education
This schematic shows how various stakeholders can be engaged when devising how schools should design outdoor learning environments. Charts and graphics: Los Angeles County Office of Education
Any guideline, the report states, begins with identifying the project team, its goals, schedule, and budget. Site assessments should include stakeholders and AEC professionals.
To encourage stakeholder engagement, the report is big on conducting workshops that establish the project’s vision, share images, and gather input. Workshops can help to keep teachers abreast of a project’s progress and serve as forums for comment about opportunities related to outdoor learning environments. The report also recommends a “student visioning exercise” in the form of a video that teachers create and show to students, to assist in customizing the learning experience.
At the conclusion of this process, districts will be able to update their Local Control and Accountability Plan to include outdoor learning, which can be incorporated into safety protocols for reopening schools.
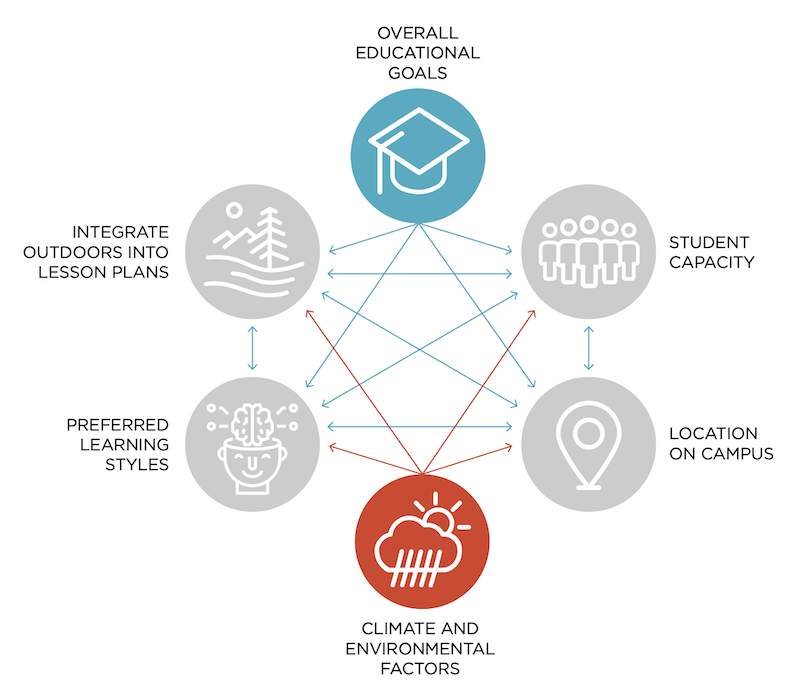 Setting goals for outdoor learning environments must consider many factors.
Setting goals for outdoor learning environments must consider many factors.
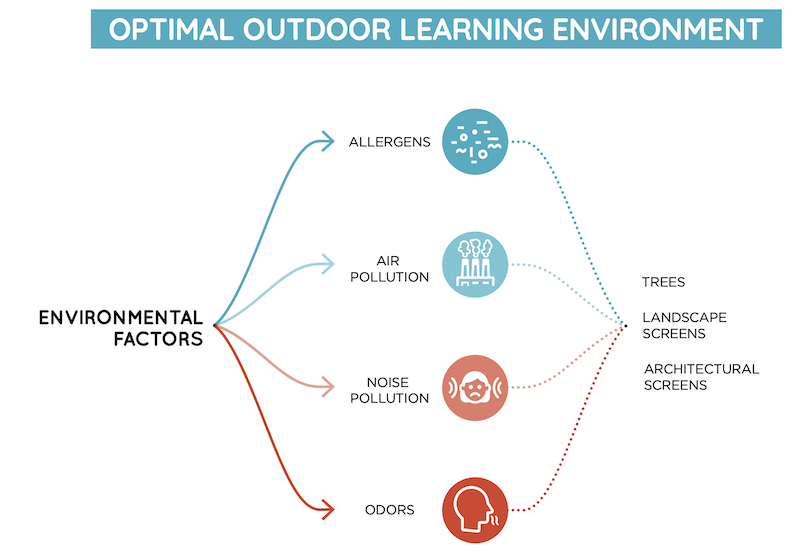
WEIGHING PROS AND CONS OF SPACE COMPONENTS
The bulk of the county’s report focuses on outdoor learning space components that include:
Seating: Student seating is one of the key components to having agility for the space. But there are any number of factors to consider: Will the seating remain outdoors, or be moved to a different location each day? Will chairs be chained together and fixed to security points? Can natural elements, like large rocks or tree stumps, serve as seating? Can seating double as desks for students? The report also provides guidelines and considerations for the use of existing furniture, built-in benches, and seat walls.
Shade and Protection. After an assessment of site conditions, the school community must decide its level of tolerance for varying environmental conditions and then the extent to protect the outdoor learning environment from them. The extent of overhead cover needed, for example, can impact the schedule, scope, and budget for a project. The different types of overhead cover to consider are permanent or temporary, fixed or movable, architectural or landscape, or a combination of the two.
The Department of State Architect (DSA), the regulatory agency overseeing public school design and construction in California, has streamlined its review and approval of these structures, which nevertheless must comply with current codes for accessible paths of travel, grading and drainage, restroom location/accessibility, and their distance from the school. The report provides guidelines for umbrellas, tents, and custom shade structures, all of which should be wind- and weather-resistant.
Teaching tools and resources. The report offers considerations and recommendations for the outdoor use of individualized rolling storage, movable water supplies, outdoor white and black boards, outdoor storage (“prefabrication options can be inexpensive,” the report suggests), and power ports.
Space definitions. Defining boundaries around the outdoor learning space “can help to delineate between different activities taking place in an outdoor setting,” the report states. Elements that can define these spaces include movable walls, permanent walls and fences (anything higher than 4 ft requires DSA approval), and planting screens and boxes. The report suggests that districts think about including solar-powered ports in the design and construction of these barriers.

The design guidelines advise that the parameters and programming for outdoor learning be established early.
Site landscaping. The report contends that the physical proximity to plants, and the wildlife attracted to them, helps reduce student anxiety, depression, and stress that can inhibit focus and motivation.
“Students concentrate better when they are not distracted by discomfort and irritation,” says the report. “Plants, such as trees and shrubs, enhance physical comfort. They provide shade, filter airborne pollutants, screen out glare, generate refreshing sounds, and create a soothing sense of human scale.” The report’s guidelines aim to protect plants and their survival, and assert that projects should identify species best suited to the growing conditions of the school.
Site infrastructure and Construction. The report offers guidelines for providing outdoor learning environments with water, electrical power, and technology. It touches as well on the logistics of construction. “The key for any contractor is to remember that we are guests in your home. As such, the approach for projects that entail site work and utility replacement on operational campuses is to carefully coordinate construction activities with school staff relating to the daily school schedule.” Minimizing disruption with an eye toward safety and health are the goals.
The report urges school districts to include outdoor learning experiences in their funding and bidding proposals, and notes that, since last December, school districts may award contracts up to $50,000 directly to consultants without going through a public bid process. For construction or reconstruction of facilities, the bid threshold is $15,000.
To test their design process, school districts should follow three steps that take a broad overview of the outdoor learning environments they want to create, define the primary program to figure out where best to locate this space, and develop multiple schemes with a priority list of components and a program for outdoor learning.
As part of their designs, the report recommends that districts include systems of modular blocks to provide a flexible solution for many component types.
Related Stories
| May 18, 2011
Former Bronx railyard redeveloped as shared education campus
Four schools find strength in numbers at the new 2,310-student Mott Haven Campus in New York City. The schools—three high schools and a K-4 elementary school—coexist on the 6.5-acre South Bronx campus, which was once a railyard.
| May 18, 2011
Eco-friendly San Antonio school combines history and sustainability
The 113,000-sf Rolling Meadows Elementary School in San Antonio is the Judson Independent School District’s first sustainable facility, with green features such as vented roofs for rainwater collection and regionally sourced materials.
| May 18, 2011
New Reform Jewish Independent school opens outside Boston
The Rashi School, one of only 17 Reform Jewish independent schools in North American and Israel, opened a new $30 million facility on a 166-acre campus shared with the Hebrew SeniorLife community on the Charles River in Dedham, Mass.
| May 18, 2011
Addition provides new school for pre-K and special-needs kids outside Chicago
Perkins+Will, Chicago, designed the Early Learning Center, a $9 million, 37,000-sf addition to Barrington Middle School in Barrington, Ill., to create an easily accessible and safe learning environment for pre-kindergarten and special-needs students.
| May 18, 2011
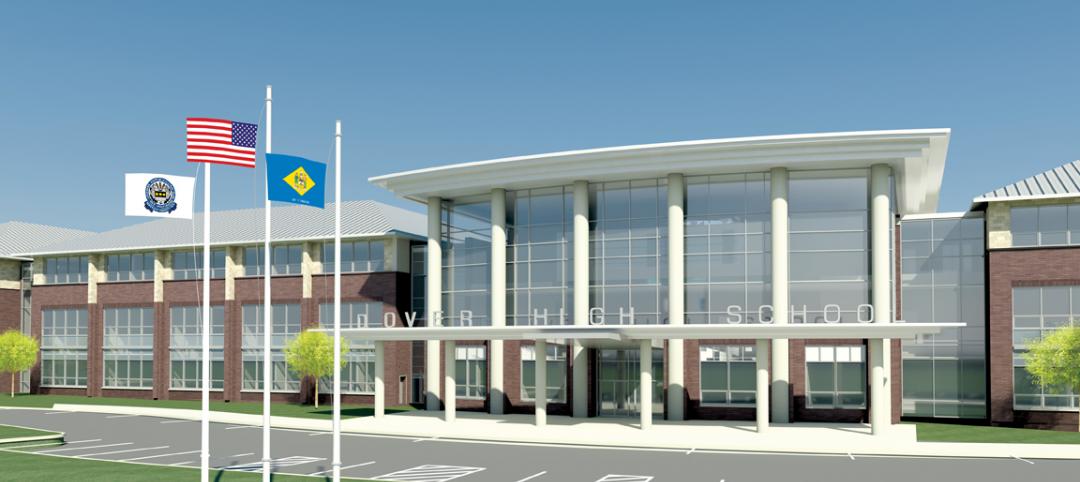
One of Delaware’s largest high schools seeks LEED for Schools designation
The $82 million, 280,000-sf Dover (Del.) High School will have capacity for 1,800 students and feature a 900-seat theater, a 2,500-seat gymnasium, and a 5,000-seat football stadium.
| May 17, 2011
Sustainability tops the syllabus at net-zero energy school in Texas
Texas-based firm Corgan designed the 152,200-sf Lady Bird Johnson Middle School in Irving, Texas, with the goal of creating the largest net-zero educational facility in the nation, and the first in the state. The facility is expected to use 50% less energy than a standard school.
| May 16, 2011
USGBC and AIA unveil report for greening K-12 schools
The U.S. Green Building Council and the American Institute of Architects unveiled "Local Leaders in Sustainability: A Special Report from Sundance," which outlines a five-point national action plan that mayors and local leaders can use as a framework to develop and implement green schools initiatives.
| May 10, 2011
Greenest buildings: K-12 and commercial markets
Can you name the nation’s greenest K-12 school? How about the greenest commercial building? If you drew a blank, don’t worry because our friends at EarthTechling have all the information on those two projects. Check out the Hawai’i Preparatory Academy’s Energy Lab on the Big Island and Cascadia Green Building Council’s new Seattle headquarters.
| Mar 15, 2011
Passive Strategies for Building Healthy Schools, An AIA/CES Discovery Course
With the downturn in the economy and the crash in residential property values, school districts across the country that depend primarily on property tax revenue are struggling to make ends meet, while fulfilling the demand for classrooms and other facilities.
| Feb 23, 2011
“School of Tomorrow” student design competition winners selected
The American Institute of Architecture Students (AIAS) and Kawneer Company, Inc. announced the winners of the “Schools of Tomorrow” student design competition. The Kawneer-sponsored competition, now in its fifth year, challenged students to learn about building materials, specifically architectural aluminum building products and systems in the design of a modern and creative school for students ranging from kindergarten to sixth grade. Ball State University’s Susan Butts was awarded first place and $2,500 for “Propel Elementary School.”