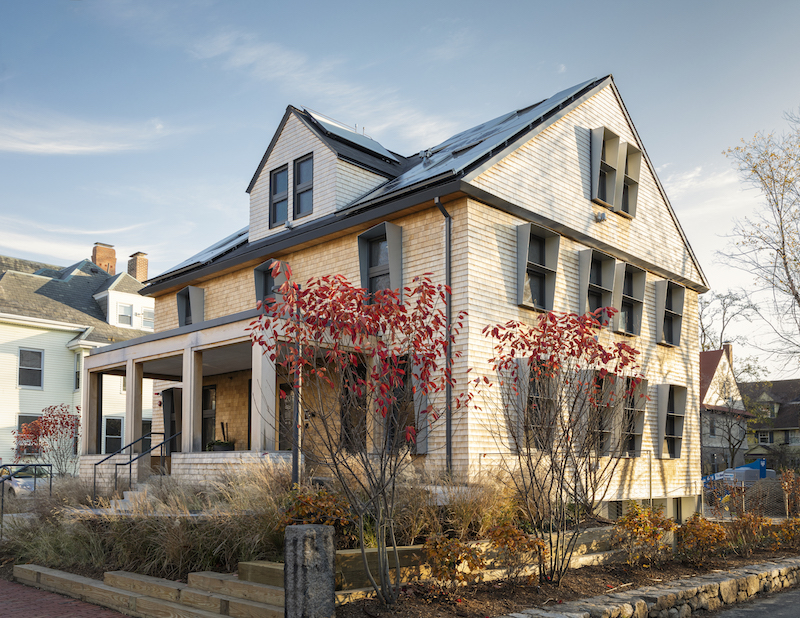
The Harvard Center for Green Buildings and Cities (CGBC) has completed the retrofitting of its 4,600-sf headquarters in Cambridge, Mass., built in 1924, into a living laboratory called HouseZero, whose design is driven by ambitious performance targets that include nearly zero energy use for heating and cooling, zero electrical lighting during the day, operating with 100% natural ventilation, and producing zero carbon emissions.
Snohetta was this project’s chief architect, and Skanska Teknikk Norway its lead energy engineer.
A prototype, HouseZero has been set up to address a chronic problem within the built environment: inefficient existing structures. The building inventory in the U.S. is estimated to account for 40% of the country’s energy consumption, with 25% of that usage attributed to housing alone. The annual costs of residential energy consumption are enormous: $230 billion for heating, cooling and powering the nation’s 113.6 million households.
CGBC, at the Harvard Graduate School of Design, has embedded hundreds of sensors connected by several miles of wiring within each component of HouseZero, from which it will draw data points that inform its researchers about the building’s behaviors. These data will be the basis of computational simulations for fuel research that could help the Center develop new systems and algorithms that promote energy efficiency, health, and sustainability.
The goal of HouseZero is to create a blueprint for reducing energy demands and increasing cost savings for property owners. “HouseZero challenged us to rethink the conventions of building design and operation to enhance lifelong efficiency and quality of life for occupants,” says Ali Malkawi, founding director of CGBC, and creator and leader of the HouseZero project.
An example of this rethinking is natural ventilation that is controlled by a window actuation system that employs sophisticated software and sensors arrays to automatically open and close windows to maintain a quality internal environment throughout the year. The building itself will strive for best possible comfort. However, Malkawi notes, a window can always be opened manually to ensure individual comfort.
HouseZero’s third floor features a flexible, highly-controlled and monitored experimental space—dubbed the LiveLab—that’s hardwired to the building’s energy exchange system. The space will allow for the testing, swapping, and optimization of new technologies. An immediate goal is to beta test new technologies that can eventually replace the building’s ground source heat pump for peak conditions.
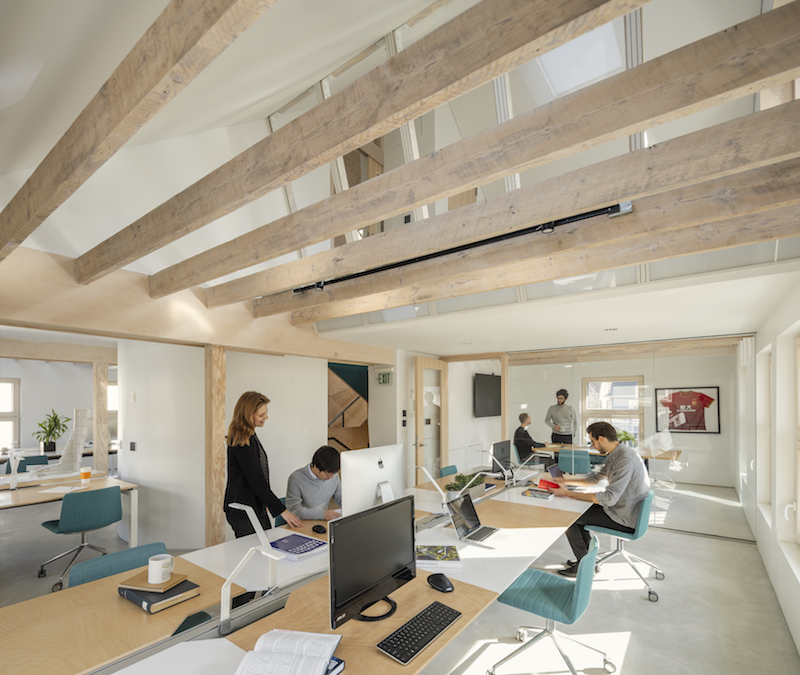

HouseZero is naturally ventilated, and designed to use only natural lighting during the daytime hours. Image: Michael Grimm
The building will also be used to research how structures connect with and respond to its natural environment. Its envelope and materials were designed to interact with the seasons and the exterior environment. The building, according to CGBC, will adjust itself to reach thermal comfort for its occupants.
HouseZero will achieve zero net energy with the help of a rooftop PV array that provides renewable electrical energy for the heat pump as well as for energy required by user equipment. A battery system is employed for night time use and low-sun conditions.
To meet proposed emission cuts of the Paris agreement, HouseZero will offset the hidden emissions generated throughout the building’s anticipated 60-year life cycle, from the fabrication and transport of building materials and construction processes, to maintenance and decommissioning.
The rest of the renovation team on this project included Columbia Construction (CM), Silman Associates (SE), BR+A (MEP/FP/lighting), Bristol Engineering (CE), WindowMaster (BAS/Controls/Natural Ventilation systems), Brekke & Strand Akustikk (acoustrics), Jensen Hughes (code and accessibility consultant), Haley & Aldrich (geotechnical engineer), Syska Hennessy (vertical transportation), Kalin Associates (specifications), Siemens Building Technologies (security systems), Solect Energy (photovoltaic systems), Reed Hilderbrand (landscape architect), Harvard Planning and Project Management; CSL Consulting (project management), and Harvard Graduate School of Design (operations support).
Related Stories
Sponsored | Resiliency | Jan 24, 2022
Blast Hazard Mitigation: Building Openings for Greater Safety and Security
Coronavirus | Jan 20, 2022
Advances and challenges in improving indoor air quality in commercial buildings
Michael Dreidger, CEO of IAQ tech startup Airsset speaks with BD+C's John Caulfield about how building owners and property managers can improve their buildings' air quality.
3D Printing | Jan 12, 2022
Using 3D-printed molds to create unitized window forms
COOKFOX designer Pam Campbell and Gate Precast's Mo Wright discuss the use of 3D-printed molds from Oak Ridge National Lab to create unitized window panels for One South First, a residential-commercial high-rise in Brooklyn, N.Y.
Sponsored | BD+C University Course | Jan 12, 2022
Total steel project performance
This instructor-led video course discusses actual project scenarios where collaborative steel joist and deck design have reduced total-project costs. In an era when incomplete structural drawings are a growing concern for our industry, the course reveals hidden costs and risks that can be avoided.
Architects | Dec 20, 2021
Digital nomads are influencing design
As our spaces continue to adapt to our future needs, we’ll likely see more collaborative, communal zones where people can relax, shop, and work.
Urban Planning | Dec 15, 2021
EV is the bridge to transit’s AV revolution—and now is the time to start building it
Thinking holistically about a technology-enabled customer experience will make transit a mode of choice for more people.
Healthcare Facilities | Dec 15, 2021
MEP design considerations for rural hospitals
Rural hospitals present unique opportunities and challenges for healthcare facility operators. Oftentimes, the infrastructure and building systems have not been updated for years and require significant improvements in order to meet today’s modern medical demands. Additionally, as these smaller, more remote hospitals are acquired by larger regional and national healthcare systems, the first step by new ownership is often to update and rehabilitate the building. But how can this be done thoughtfully, economically, and efficiently in ways that allow the engineering and facility staff to adapt to the changes? And how can the updates accurately reflect the specific needs of rural communities and the afflictions with which these areas most commonly face?
Sponsored | BD+C University Course | Oct 15, 2021
7 game-changing trends in structural engineering
Here are seven key areas where innovation in structural engineering is driving evolution.
Sponsored | Glass and Glazing | Oct 1, 2021
Seizing the Daylight with BIPV Glass
Glass has always been an idea generator. Now, it’s also a clean energy generator.
Glass and Glazing | Sep 30, 2021
Plans move forward on Central Place Sydney, duel towers with an AI-driven façade system
SOM and Fender Katsalidis are designing the project.