|
| Lincoln Center’s walkable green roof is scheduled to debut next spring. The roof, in the form of a hyperbolic paraboloid, will reach a full height of 11 feet from the plaza level and 23 feet from the sidewalk level; it will extend down to the plaza on the south end, providing access for pedestrians. The cross section below depicts the composition of the green roof system. |
 |
27. Next-Generation Green Roofs Sprout up in New York
New York is not particularly known for its green roofs, but two recent projects may put the Big Apple on the map.
In spring 2010, the Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts will debut one of the nation's first fully walkable green roofs. Located across from the Juilliard School in Lincoln Center's North Plaza, Illumination Lawn will consist of a glass-walled restaurant topped with a 10,000-sf, sloped vegetated roof that will double as a campus lawn for students and the public.
The sloped green roof will add some much-needed softness to the hardscape that dominates Lincoln Center. "It will be a dynamic, engaging kind of space that people hopefully will want to run up on, play Frisbee, or relax," says Heidi Blau, AIA, LEED, partner with FXFOWLE Architects, which is collaborating with Diller Scofidio + Renfro on the Lincoln Center redevelopment.
To support the weight and handle the wear and tear from constant foot traffic, the design team specified a beefed-up version of a typical green roof system. A six-inch-thick composite poured-concrete/metal-deck structural slab rated for 100-pound live loads will support the 14-inch-thick vegetated roof. The slab will be supported on nine steel columns with five girders and 45 beams situated to create the saddle-like "hypar" roof shape. More on Illumination Lawn.
 |
| High-end condos at the 101 Warren St. mixed-use development in New York overlook a rooftop urban forest, complete with 101 pine trees. |
Four miles downtown, in Manhattan's Tribeca neighborhood, a new 950,000-sf mixed-use condo tower designed by Skidmore, Owings and Merrill features what can only be described as a miniature urban forest atop the building's five-story podium. SOM teamed with local landscape architect Thomas Balsley Associates to develop the intensive green roof, which is composed of 101 Austrian pines—some reaching 35 feet in height—planted in a soil bed up to 42 inches deep.
The entire green roof system—which includes a 12- to 16-inch-thick concrete slab topped with a 2 mm waterproof membrane, a root barrier, four inches of rigid insulation, a three-inch-thick drainage panel, geotextile fabric, planting soil, and three inches of mulch—extends six feet deep in certain areas—a depth that has been proven to be sufficient in urban settings and broad planting areas, says Thomas Balsley. He estimates that the trees will eventually reach 50 feet in height.
All residents of the 31-story 101 Warren St. condo tower have access to the rooftop pine forest, and many ultra-lux units overlook the trees. The building's developer, Edward Minskoff, was willing to take on the extra cost of the urban forest because of the unique selling point it offered to prospective condo buyers. It also gave tenants some much-needed green space.
"The notion of a garden in the sky is very appropriate to the urban condition in New York, where the ground plane is precious and, therefore, the opportunities for semi-public space is explored in the third dimension," says Mustafa K. Abadan, FAIA, SOM partner in charge on the project.28. New LEED Retail Programs Speed up Certification
The U.S. Green Building Council's stated goal of reaching 100,000 LEED-certified buildings by 2010 will require thousands of new commercial buildings certified in the next six months. The building type that goes up fastest in the largest numbers is retail commercial buildings. Retail buildings have been LEED registered as prototypes since 2005, but LEED for Retail Commercial Interiors and LEED for Retail New Construction, now open for member ballot, would allow much more flexible certification.
The USGBC is also publishing a LEED for Retail Best Practices manual, to illustrate the strategies used by companies in the LEED for Retail pilot. Any green feature that isn't repeatable for a large number of stores is meaningless in retail, so best practices are even more important than in other building types. Some of the companies participating include Office Depot (LEED Silver in its Austin, Texas, store with six other similar stores), McDonald's (several LEED-certified restaurants), and Chipotle (the world's first LEED Platinum, in Gurnee, Ill.). |
| When the green light is on (circled above), building occupants know it’s okay to open the windows because outdoor air will moderate the building’s mechanical system performance. |
29. Notification System gives Teachers the Green Light to Open the Windows
One of the biggest complaints among K-12 school facility managers is the conflict that arises when teachers and students open the windows during not-so-ideal climate conditions. Introducing outside air into a conditioned building can decrease the mechanical system's efficiency if the outdoor climate conditions increase heating or cooling demands already being made on the mechanical system.
Since most K-12 school districts don't have the budget for high-end automated climate controls, communication and education are often the only tools facility managers have to prevent occupants from opening the windows during less-than-optimal weather conditions.
To help some of its K-12 school clients minimize energy costs, NAC¦Architecture has implemented a simple, inexpensive notification system made up of red and green lights located in the corridors. When the green lights are on, the windows can be opened to help cool the classroom spaces. When the red lights are on, all windows should remain shut, as outdoor air will inhibit the mechanical system's ability to properly condition the building.
"This system is an economical approach to the age-old quandary regarding operable windows," says Dana L. Harbaugh, AIA, LEED, principal architect with NAC¦Architecture, who developed the system. "It asks building users to facilitate environmental stewardship on a daily basis, raising awareness of their impact on energy usage."
Related Stories
AEC Tech | May 1, 2023
Utilizing computer vision, AI technology for visual jobsite tasks
Burns & McDonnell breaks down three ways computer vision can effectively assist workers on the job site, from project progress to safety measures.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 27, 2023
BD+C's 2023 Design Innovation Report
Building Design+Construction’s Design Innovation Report presents projects, spaces, and initiatives—and the AEC professionals behind them—that push the boundaries of building design. This year, we feature four novel projects and one building science innovation.
Building Technology | Apr 24, 2023
Let’s chat about AI: How design and construction firms are using ChatGPT
Tech-savvy AEC firms that already use artificial intelligence to enhance their work view the startling evolution of ChatGPT mostly in a positive light as a potential tool for sharing information and training employees and trade partners. However, the efficacy of ChatGPT is likely to rest on the construction industry’s aggregation of quality data that, until recently, has been underwhelming for getting the greatest bang from AI and machine learning.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 19, 2023
HDR uses artificial intelligence tools to help design a vital health clinic in India
Architects from HDR worked pro bono with iKure, a technology-centric healthcare provider, to build a healthcare clinic in rural India.
3D Printing | Apr 11, 2023
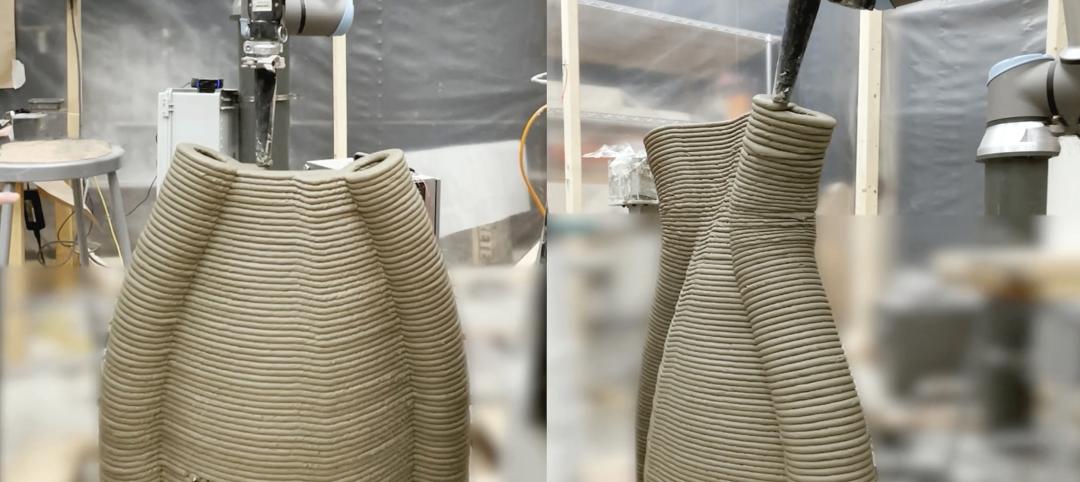
University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory unveils Shell Wall—a concrete wall that’s lightweight and freeform 3D printed
The University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory has unveiled a new product called Shell Wall—which the organization describes as the first lightweight, freeform 3D printed and structurally reinforced concrete wall. The innovative product leverages DART Laboratory’s research and development on the use of 3D-printing technology to build structures that require less concrete.
Contractors | Apr 10, 2023
What makes prefabrication work? Factors every construction project should consider
There are many factors requiring careful consideration when determining whether a project is a good fit for prefabrication. JE Dunn’s Brian Burkett breaks down the most important considerations.
Smart Buildings | Apr 7, 2023
Carnegie Mellon University's research on advanced building sensors provokes heated controversy
A research project to test next-generation building sensors at Carnegie Mellon University provoked intense debate over the privacy implications of widespread deployment of the devices in a new 90,000-sf building. The light-switch-size devices, capable of measuring 12 types of data including motion and sound, were mounted in more than 300 locations throughout the building.
Cladding and Facade Systems | Apr 5, 2023
Façade innovation: University of Stuttgart tests a ‘saturated building skin’ for lessening heat islands
HydroSKIN is a façade made with textiles that stores rainwater and uses it later to cool hot building exteriors. The façade innovation consists of an external, multilayered 3D textile that acts as a water collector and evaporator.
Project + Process Innovation | Mar 22, 2023
Onsite prefabrication for healthcare construction: It's more than a process, it's a partnership
Prefabrication can help project teams navigate an uncertain market. GBBN's Mickey LeRoy, AIA, ACHA, LEED AP, explains the difference between onsite and offsite prefabrication methods for healthcare construction projects.
Building Tech | Mar 14, 2023
Reaping the benefits of offsite construction, with ICC's Ryan Colker
Ryan Colker, VP of Innovation at the International Code Council, discusses how municipal regulations and inspections are keeping up with the expansion of off-site manufacturing for commercial construction. Colker speaks with BD+C's John Caulfield.